The Lodzkie Region – in the centre of Poland
in the centre of Europe











GDP per capita in 2023
5.9%


Average gross salary (as for October 2025)
PLN 8,161
approx. €1,915 and $2,230

Most important universities
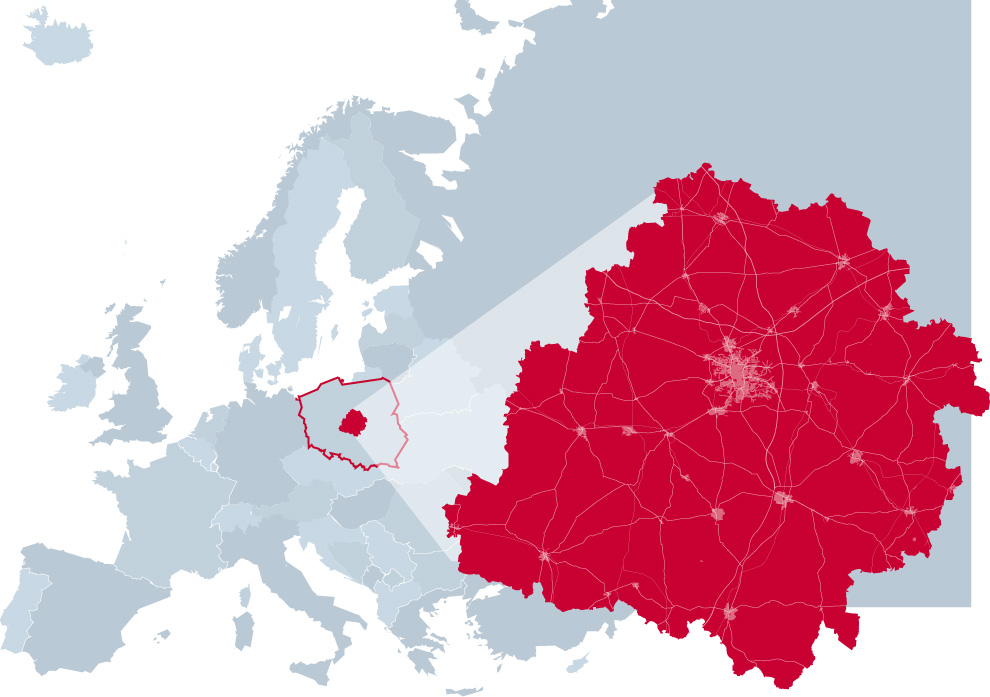
The Lodzkie Region - close to everywhere
Everything is close to the Lodzkie Region, because the region is situated in the centre of Poland, in the centre of Europe and has excellent transport connections
Almost all major Polish cities are within 200 km, and almost all European capitals are within 1500 kilometers.
Infrastructure

An advantage of the Lodzkie Region is its location in the middle of Poland and Europe. Owing to this central geographical location, the region has excellent transport connections to Polish and foreign cities (first place in Poland in terms of kilometres of highways, second place in terms of the aggregate kilometrage of highways and expressways). The Lodzkie Region lies at the intersection of the A1 and A2 highways, which are part of the Trans-European Transport Network (TEN-T) connecting Western Europe with Eastern Europe (North Sea-Baltic Corridor), and the Baltic countries with the southern part of the continent (Baltic-Adriatic Corridor).
The S8 expressway to the south of Lodz and the S14 expressway (west of the city) are also roads of international importance, and the capital of the region is the first city in Poland with a full ring of top-category roads.
You can go from Warszawa to Łódź via the A2 motorway in just over an hour, while the journey via the A1 motorway from Łódź to Gdańsk takes about three hours. In contrast, you can get to Wrocław with the S8 expressway within 2 hours.

Important national railway routes run through the Lodzkie Region. These are the lines: E20 Warszawa - Kutno - Poznań, the Central Rail Line linking the capital with Silesia and Cracow, and the Coal Trunk - Line connecting Karsznice, Zduńska Wola, Inowroclaw and Gdynia. Another important node is Koluszki, which connects Łódź with Warsaw, Lublin, Katowice and Cracow.
The region's railway window on the world is the terminal at Łódź-Olechów. This is one of the most important cargo reloading terminals in Poland. Thanks to the launch of this terminal, trade with the Chinese city of Chengdu in Sichuan province is developing dynamically. The route of the "New Silk Route" (as the Chinese call it) runs from Chengdu through Kazakhstan, Russia and Belarus to Lodz. The Chinese have chosen Łódź from among other locations because it is situated in the centre of Europe and goods can get to France, Scandinavia, Russia or the Balkans in two days. A "local embassy" takes care of the development of Chinese relations, i.e. The Regional Office of the Lodzkie Region and the City of Lodz in Chengdu, which helps to establish economic contacts and scientific and cultural promotion.
An advantage of the Lodzkie Region is Łódzka Kolej Aglomeracyjna (Lodz Agglomeration Railway), appointed by the regional authorities. Łódzka Kolej Aglomeracyjna (Lodz Agglomeration Railway) transports tourists, students and workers to the most distant parts of the region. The routes include: Łódź - Toruń, Łódź - Sieradz, Łódź - Poznań, Łódź - Łowicz, Łódź - Warszawa, Łódź - Radomsko and Łódź - Kutno.
New Łódź-Fabryczna railway underground station, situated in the centre of the city, is the biggest and one of the most modern facilities of its kind in Europe. In few years it will be a key element of the New Centre of Łódź. In March 2021, the construction of a high-speed cross-diameter tunnel (the so-called small metro) began. The tunnel will run under the center of Łódź and will connect the Łódź-Fabryczna Railway Station with Łódź-Kaliska and Łódź - Żabieniec stations. The railway connections created in this way will be an important element of the transport and logistics system of the Central Communication Port near Warsaw.

There is an international airport 6 kilometres from the centre of Łódź - Lodz Wladyslaw Reymont Airport. The network of flight connections is developing dynamically. The Lodz airport mainly serves connections to the west (Great Britain, Ireland, Belgium) and south (Spain, Italy). There is also a cargo terminal at the airport, which in 2022 cleared approx. 5,5 tons of freight and was in second place among Polish airports in the RFS transport (Road Feeder Service).
Within a 10-minute drive from the centre of Lodz, there is the Lodz Airport Central Poland which operates passenger and cargo traffic. And in Warsaw, 130 km away, there is the Warsaw Chopin Airport, where you can head out to more than a hundred destinations around the globe.
Economy

On the territory of the Lodzkie Region there are about 290 thousand economic entities, mainly small and medium. These companies may be potential contractors and partners (as sub-suppliers of parts and accessories) for foreign investors in the field of trade and investment cooperation.
Over 97% of all entities are private companies. The number of commercial companies with foreign capital share is about 1,900.The Lodzkie Region has a strong economy which is continually developing new branches.
It is traditionally strong in light industry and in industries such as household appliances, production of construction materials, and agricultural and food processing.
The Lodzkie Region is among the most important Polish centres bringing together companies from the sector of modern services for business (BPO/SSC).
Another industry is the power industry, the main centre of which is Bełchatów, where more than 20% of domestic electricity is produced.
Lodz is one of the most important Polish centres for external business support. According to the ABSL report "Sector of modern business services in Poland 2020", BPO and SSC companies employed almost 30 thousand people in the capital of the region, that is 8.9% of all employees of this sector in Poland.
Another key sector for the region is logistics, which is no surprise given its strategic location. The biggest logistics centre in the region is Stryków, partly due to the fact that it is situated at the intersection of the A1 and A2 motorways. The following logistics parks have been created there: Business Park, Segro Logistic Park Stryków, Tulipan Park Stryków, Panattoni Park Stryków and registered offices of the companies in this industry. The second place with logistics importance is Piotrków Trybunalski. Also here there are logistics parks. They include: Logistic City Piotrkow Distribution Center, P3 Park Piotrkow, Kaufland Logistic Center, Regional Distribution Center IKEA, ProLogis Park Piotrkow.
Education

The capital of the region is an important academic centre. Six state universities are established in Łódź: Lodz University of Technology, University of Lodz, Medical University of Lodz, the Grażyna and Kiejstut Bacewicz Academy of Music in Lodz, Wladyslaw Strzemiński Academy of Fine Arts in Lodz and the Polish National Film, Television and Theatre School in Lodz. The latter is a school with a long tradition, one of the oldest schools in the world that educates directors, cameramen, animation authors, editors, scenarists, photogrphers and actors. In Łódź there are 21 private universities. More than 100 thousand people study in the capital of the region. 18 thousand highly qualified graduates enter the labour market annually.
In the 2023/2024 academic year, in the capital of the region and in the province there were 69.82 thousand students.
Education in the Lodzkie Region means also centres of international scientific cooperation: Alliance Française, British Council, the Department of German Studies, the Department of American Studies and Mass Media, School of Polish for Foreigners of University of Lodz. In addition to the universities, important research centres in R&D are located in the region, including representations of the Polish Academy of Sciences: the Centre of Molecular and Macromolecular Studies of the Polish Academy of Sciences, Institute of Medical Biology of the Polish Academy of Sciences, Centre of Medical Biology and Microbiology of the Polish Academy of Sciences. In Łódź there is a school for children and youth at the British International School of the University of Łódź conducting educational activities in English, according to the English National Curriculum. The curriculum covers all stages of an English education for children and youth aged 3 to 18 years.